Discovery commands
Multiple commmands to discover information about a Minecraft server, such as IP address, location, and DNS records, among others.

MCPTool is the best pentesting tool for Minecraft servers. It is a powerful tool that allows you to test your server's security and vulnerabilities.
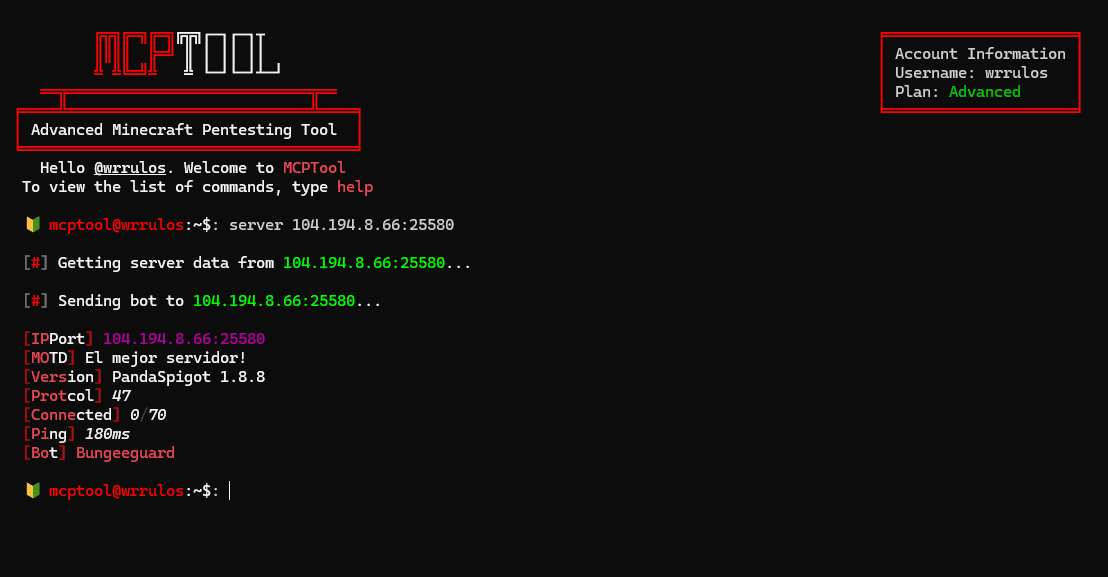
The definitive tool to automate the security audit of your Minecraft server, providing easy and complete access to the techniques and functionalities most used by griefers.
Multiple commmands to discover information about a Minecraft server, such as IP address, location, and DNS records, among others.
Easily perform professional scans on Minecraft servers to identify vulnerabilities and security flaws, such as open ports and services running on the server.
Create a fakeproxy server to intercept and manipulate the messages and commands sent between the client and the server.

Use the latest exploits to test the security of your Minecraft server and identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by griefers.
Test the resistance of your Minecraft server to a simple bot attack, simulating the behavior of a botnet.
MCPTool is available in multiple languages, making it easier for users from different countries to use the tool.
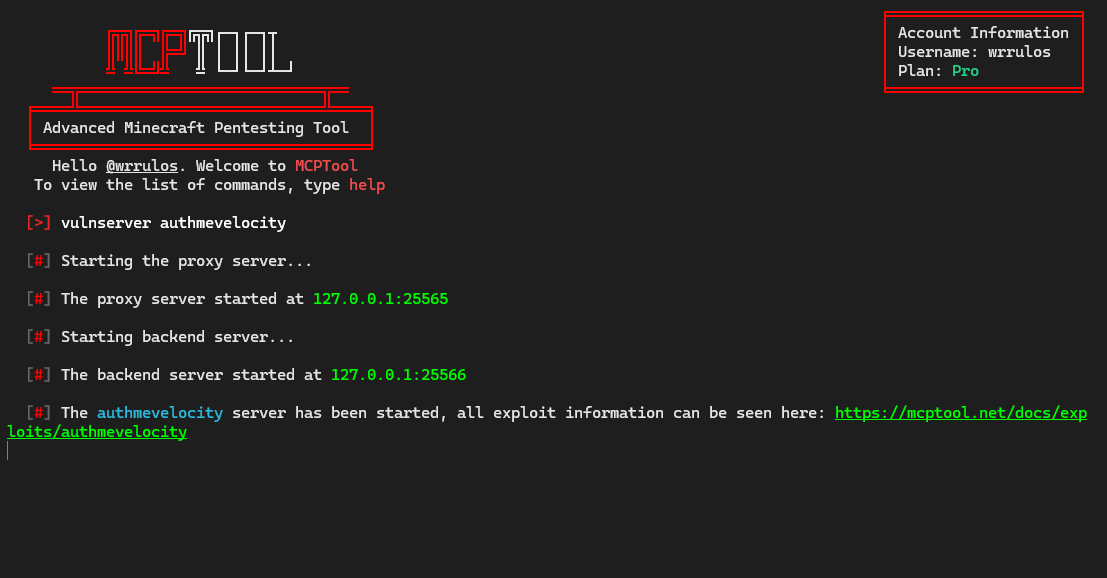
You can create vulnerable servers to test exploits and understand how they work.
You can check if you or your friend were exposed to server database leaks.
Reasons why you should choose MCPTool to automate the security audit of your Minecraft server.
MCPTool provides easy and complete access to the techniques and functionalities most used by griefers. Don't waste your time with manual tasks, automate your security audit.
Our team is always ready to help you with any questions or issues you may have. We provide support to all our users, no matter the plan you choose.
We continuously update MCPTool with new features and improvements to provide you with the best experience. You will always have access to the latest functionalities.
Choose the plan that works for you
per month
Ideal for testing MCPTool and getting started with the basics
lifetime
Life-time access to all the features and updates
per month
Ideal for creators who promote or make videos about the tool
Here are some reviews from our customers
5.0
"Just Bought MCPTool, pretty fast service the tool is nice and im lookin forward to see the future updates!"
5.0
"Really like the software, and excellent service too, worth every dollar"
5.0
"The tool is amazing, with the upgrade is the best!, very recommended!!!"
5.0
"I really liked the service, crazy product worth the money"
5.0
"The tool is very useful, and able to do so much stuff, like A LOT and it's so legit!"
5.0
"Perfecta herramienta muy rapido y sencillo 100% recomendado"
Here are some of the partners we work with

